|
This is an example of the techniques we have used in
previous lessons to save individual data of primitive types:
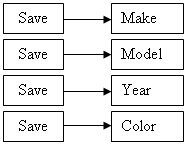
The values can be retrieved with the following code:
using namespace System;
using namespace System::IO;
int main()
{
String ^Make, ^Model;
int Year, Color;
FileStream ^ stmCar = gcnew FileStream(L"FordEscort.car",
FileMode::Open);
BinaryReader ^ bnrCar = gcnew BinaryReader(stmCar);
try {
Console::WriteLine(L"Make: {0}", bnrCar->ReadString());
Console::WriteLine(L"Model: {0}", bnrCar->ReadString());
Console::WriteLine(L"Year: {0}", bnrCar->ReadInt32());
Console::Write(L"Color: ");
int clr = bnrCar->ReadInt32();
switch(clr)
{
case 1:
Console::WriteLine(L"Black");
break;
case 2:
Console::WriteLine(L"Gray");
break;
case 3:
Console::WriteLine(L"White");
break;
case 4:
Console::WriteLine(L"Red");
break;
case 5:
Console::WriteLine(L"Blue");
break;
}
}
finally
{
bnrCar->Close();
stmCar->Close();
}
return 0;
}
This would produce:
Make: Ford
Model: Escort
Year: 1998
Color: Black
Press any key to continue . . .
In the same way, we learned to save the individual fields of
a class:
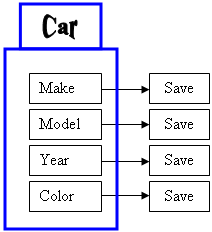
Here is an example:
using namespace System;
using namespace System::IO;
public ref class CCar
{
public:
String ^ Make;
String ^ Model;
int Year;
int Color;
CCar();
};
CCar::CCar()
{
Make = L"Toyota";
Model = L"Corolla";
Year = 2002;
Color = 2;
}
int main()
{
CCar ^ vehicle = gcnew CCar;
FileStream ^ stmCar = File::Create(L"ToyotaCorolla.car");
BinaryWriter ^ bnwCar = gcnew BinaryWriter(stmCar);
try {
bnwCar->Write(vehicle->Model);
bnwCar->Write(vehicle->Year);
bnwCar->Write(vehicle->Color);
}
finally
{
bnwCar->Close();
stmCar->Close();
}
return 0;
}
When it comes to a class, the problem with saving individual
fields is that you could forget to save one of the fields. For example,
considering a Car class, if you don't save the Make information of a Car object
and retrieve or open the saved object on another computer, the receiving user
would miss some information and the car cannot be completely identifiable. An
alternative is to save the whole Car object.
Object serialization consists of saving a whole object as
one instead of its individual fields:
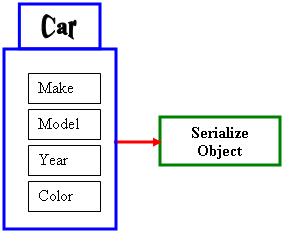
In other words, a variable declared from a class can be
saved to a stream and then the saved object can be retrieved later or on another
computer. The .NET Framework supports two types of object
serialization: binary and SOAP.
|
 Practical
Learning: Introducing Serialization Practical
Learning: Introducing Serialization |
|
- Start Microsoft Visual C++ and create a new CLR empty project named GeorgetownCleaningServices7
- To add a new source file to the project, on the main menu, click Project
-> Add New Item...
- In the Templates list, click C++ File (.cpp)
- Set the Name to Exercise and click Add
- In the empty document, type the following:
using namespace System;
using namespace System::IO;
void HireEmployee()
{
FileStream ^ fsEmployee = nullptr;
BinaryWriter ^ bwEmployee = nullptr;
// Ask the clerk to enter an employee number
// using the format 00-000
Console::Write(L"Enter Employee Number (00-000): ");
String ^emplNumber = Console::ReadLine();
String ^ strPath = L"C:\\Georgetown Cleaning Services\\Employees\\"
+ emplNumber + L".gce";
if( File::Exists(strPath) )
{
Console::Write(L"\nEither the employee has already been hired, ");
Console::WriteLine(L"or there is already another employee with that number.");
return;
}
else // If no employee with that number was found, create it
{
try {
// If there is not yet a directory named Employees, then create it
Directory::CreateDirectory(L"C:\\Georgetown Cleaning Services\\Employees");
}
catch(DirectoryNotFoundException ^)
{
Console::WriteLine(L"The folder could not be created");
}
try {
fsEmployee = File::Create(strPath);
bwEmployee = gcnew BinaryWriter(fsEmployee);
Console::Write(L"Enter Employee First Name: ");
String ^emplFName = Console::ReadLine();
Console::Write(L"Enter Employee Last Name: ");
String ^emplLName = Console::ReadLine();
Console::Write(L"Enter Hourly Salary: ");
double emplSalary = double::Parse(Console::ReadLine());
// The minimum salary in this company is 7.50
if( emplSalary < 7.50 )
emplSalary = 7.50;
bwEmployee->Write(emplNumber);
bwEmployee->Write(emplFName);
bwEmployee->Write(emplLName);
bwEmployee->Write(emplSalary);
}
finally
{
bwEmployee->Close();
fsEmployee->Close();
}
}
Console::WriteLine();
}
int main()
{
wchar_t answer = L'0';
do {
try {
Console::WriteLine(L"What do you want to do?");
Console::WriteLine(L"0. Quit");
Console::WriteLine(L"1. Hire a new employee");
Console::WriteLine(L"2. Process a payroll");
Console::Write(L"Your Choice: ");
answer = wchar_t::Parse(Console::ReadLine());
}
catch(FormatException ^)
{
Console::WriteLine(L"Invalid Answer!");
}
switch(answer)
{
case L'1':
HireEmployee();
break;
case L'2':
break;
default:
break;
}
} while (answer == L'1' || answer == L'2');
Console::WriteLine();
return 0;
}
|
-
Execute the application and test it. Here is an example:
What do you want to do?
0. Quit
1. Hire a new employee
2. Process a payroll
Your Choice: 1
Enter Employee Number (00-000): 86-225
Enter Employee First Name: Anne
Enter Employee Last Name: Harang
Enter Hourly Salary: 16.75
What do you want to do?
0. Quit
1. Hire a new employee
2. Process a payroll
Your Choice: 1
Enter Employee Number (00-000): 42-713
Enter Employee First Name: Peter
Enter Employee Last Name: Lansome
Enter Hourly Salary: 12.45
What do you want to do?
0. Quit
1. Hire a new employee
2. Process a payroll
Your Choice: 1
Enter Employee Number (00-000): 29-368
Enter Employee First Name: Gertrude
Enter Employee Last Name: Monay
Enter Hourly Salary: 10.85
What do you want to do?
0. Quit
1. Hire a new employee
2. Process a payroll
Your Choice: 0
Press any key to continue . . .
|
-
Close the DOS window
Binary serialization works by processing an object rather
than streaming its individual member variables. This means that, to use it, you define an object and
initialize it, or "fill" it, with the necessary values and any
information you judge necessary. This creates a "state" of the object.
It is this state that you prepare to serialize. When you save the object, it is
converted into a stream.
To perform binary serialization, there are a few steps you
must follow. When creating the class whose objects would be serialized, start it
with the [Serializable] attribute. Here is an example:
[Serializable]
public ref class CCar
{
public:
String ^ Make;
String ^ Model;
int Year;
int Color;
CCar();
};
Before serializing an object, you should reference the System::Runtime::Serialization::Formatters::Binary
namespace. The class responsible for binary serialization is called BinaryFormatter.
This class is equipped with two constructors. The default constructor is used to
simply create an object. After declaring the variable, to actually serialize an
object, call the Serialize() method of the BinaryFormatter class.
The method is overloaded with two versions. One of the versions of this method
uses the following syntax:
public:
virtual void Serialize(Stream ^ serializationStream,
Object ^ graph) sealed;
The first argument to this method must be an object of a Stream-based
class. In the previous lessons, we saw how to create Stream objects (for
example using the FileStream class).
The second argument must be the object to serialize. This
means that, before calling this method, you should have built the object.
Here is an example:
using namespace System;
using namespace System::IO;
using namespace System::Runtime::Serialization::Formatters::Binary;
[Serializable]
public ref class CCar
{
public:
String ^ Make;
String ^ Model;
int Year;
int Color;
};
int main()
{
CCar ^ vehicle = gcnew CCar;
vehicle->Make = L"Lexus";
vehicle->Model = L"LS";
vehicle->Year = 2007;
vehicle->Color = 4;
FileStream ^ stmCar = gcnew FileStream(L"LexusLS.car",
FileMode::Create);
BinaryFormatter ^ bfmCar = gcnew BinaryFormatter;
bfmCar->Serialize(stmCar, vehicle);
return 0;
}
|
 Practical
Learning: Serializing an Object Practical
Learning: Serializing an Object
|
|
- To create a new class, in the Class View, right-click GeorgetownCleaningServices7
->
Add -> Class...
- In the Templates list, click C++ Class and click Add
- Set the Name to CPayrollInformation and click Finish
- Change the PayrollInformation.h header file as follows:
#pragma once
using namespace System;
[Serializable]
public ref class CPayrollInformation
{
private:
String ^ number;
String ^ fname;
String ^ lname;
double salary;
DateTime start;
public:
CPayrollInformation(void);
property String ^ EmployeeNumber
{
String ^ get() { return this->number; }
void set(String ^ value) { this->number = value; }
}
property String ^ FirstName
{
String ^ get() { return this->fname; }
void set(String ^ value) { this->fname = value; }
}
property String ^ LastName
{
String ^ get() { return this->lname; }
void set(String ^ value) { this->lname = value; }
}
property double HourlySalary
{
double get() { return this->salary; }
void set(double value) { this->salary = value; }
}
property DateTime StartPeriod
{
DateTime get() { return this->start; }
void set(DateTime value) { this->start = value; }
}
property DateTime EndPeriod
{
DateTime get() { return start.AddDays(13); }
}
double Week1Monday;
double Week1Tuesday;
double Week1Wednesday;
double Week1Thursday;
double Week1Friday;
double Week2Monday;
double Week2Tuesday;
double Week2Wednesday;
double Week2Thursday;
double Week2Friday;
double RegularHours;
double OvertimeHours;
double RegularAmount;
double OvertimeAmount;
double TotalEarnings;
};
|
- Access the Exercise.cpp source file and change it as follows:
#include "PayrollInformation.h"
using namespace System;
using namespace System::IO;
using namespace System::Runtime::Serialization::Formatters::Binary;
void HireEmployee();
void CreatePayroll();
void SavePayroll(CPayrollInformation ^ pay);
void ShowPayroll(CPayrollInformation ^ payed);
void HireEmployee()
{
FileStream ^ fsEmployee = nullptr;
BinaryWriter ^ bwEmployee = nullptr;
// Ask the clerk to enter an employee number
// using the format 00-000
Console::Write(L"Enter Employee Number (00-000): ");
String ^emplNumber = Console::ReadLine();
String ^ strPath = L"C:\\Georgetown Cleaning Services\\Employees\\"
+ emplNumber + L".gce";
if( File::Exists(strPath) )
{
Console::Write(L"\nEither the employee has already been hired, ");
Console::WriteLine(L"or there is already another employee with that number.");
return;
}
else // If no employee with that number was found, create it
{
try {
// If there is not yet a directory named Employees, then create it
Directory::CreateDirectory(L"C:\\Georgetown Cleaning Services\\Employees");
}
catch(DirectoryNotFoundException ^)
{
Console::WriteLine(L"The folder could not be created");
}
try {
fsEmployee = File::Create(strPath);
bwEmployee = gcnew BinaryWriter(fsEmployee);
Console::Write(L"Enter Employee First Name: ");
String ^emplFName = Console::ReadLine();
Console::Write(L"Enter Employee Last Name: ");
String ^emplLName = Console::ReadLine();
Console::Write(L"Enter Hourly Salary: ");
double emplSalary = double::Parse(Console::ReadLine());
// The minimum salary in this company is 7.50
if( emplSalary < 7.50 )
emplSalary = 7.50;
bwEmployee->Write(emplNumber);
bwEmployee->Write(emplFName);
bwEmployee->Write(emplLName);
bwEmployee->Write(emplSalary);
}
finally
{
bwEmployee->Close();
fsEmployee->Close();
}
}
Console::WriteLine();
}
void CreatePayroll()
{
FileStream ^ fsPayroll = nullptr;
BinaryReader ^ brPayroll = nullptr;
DateTime dteStartDate;
CPayrollInformation ^ payroll = gcnew CPayrollInformation();
double monday1 = 0.00, tuesday1 = 0.00,
wednesday1 = 0.00, thursday1 = 0.00,
friday1 = 0.00, monday2 = 0.00,
tuesday2 = 0.00, wednesday2 = 0.00,
thursday2 = 0.00, friday2 = 0.00;
double totalHoursWeek1 = 0.00,
totalHoursWeek2 = 0.00;
double regHours1 = 0.00, regHours2 = 0.00,
ovtHours1 = 0.00, ovtHours2 = 0.00;
double regAmount1 = 0.00, regAmount2 = 0.00,
ovtAmount1 = 0.00, ovtAmount2 = 0.00;
double regularHours = 0.00, overtimeHours = 0.00;
double regularAmount = 0.00,
overtimeAmount = 0.00,
totalEarnings = 0.00;
Console::Write(L"Enter Employee Number: ");
String ^emplNumber = Console::ReadLine();
String ^ strEmployeePath = L"C:\\Georgetown "
L"Cleaning Services\\Employees\\"
+ emplNumber + ".gce";
if( !File::Exists(strEmployeePath) )
{
Console::WriteLine(L"There is no employee with "
L"that number in our records");
return;
}
// If an employee with that number was found,
// continue with the payroll
else
{
try {
fsPayroll = gcnew FileStream(strEmployeePath,
FileMode::Open,
FileAccess::Read);
brPayroll = gcnew BinaryReader(fsPayroll);
payroll->EmployeeNumber = brPayroll->ReadString();
payroll->FirstName = brPayroll->ReadString();
payroll->LastName = brPayroll->ReadString();
payroll->HourlySalary = brPayroll->ReadDouble();
Console::WriteLine(L"\n------------------------"
L"------------------------");
Console::WriteLine(L"Employee #: {0}",
payroll->EmployeeNumber);
Console::WriteLine(L"Full Name: {0}, {1}",
payroll->LastName,
payroll->FirstName);
Console::WriteLine(L"Hourly Salary: {0:C}",
payroll->HourlySalary);
Console::WriteLine(L"-------------------------"
L"-----------------------\n");
}
finally
{
brPayroll->Close();
fsPayroll->Close();
}
try {
do {
Console::Write(L"Enter Payroll Start "
L"Date (mm/dd/yyyy): ");
dteStartDate = DateTime::Parse(Console::ReadLine());
if( dteStartDate.DayOfWeek != DayOfWeek::Sunday )
{
Console::WriteLine(L"Invalid Date Entry");
Console::WriteLine(L"Payrolls start "
L"on a Sunday");
}
} while (dteStartDate.DayOfWeek !=
DayOfWeek::Sunday);
payroll->StartPeriod = dteStartDate;
}
catch(FormatException ^)
{
Console::WriteLine(L"Invalid Date Entry");
}
}
// Retrieve the value of each day worked
Console::WriteLine(L"\nEnter the time worked "
L"for each day (0.00)");
Console::WriteLine(L"=-= Week 1 =-=");
try {
Console::Write(L"{0}: ",
payroll->StartPeriod.AddDays(1).ToString(L"D"));
monday1 = double::Parse(Console::ReadLine());
}
catch(FormatException ^)
{
Console::WriteLine(L"You typed an invalid value");
}
try {
Console::Write(L"{0}: ",
payroll->StartPeriod.AddDays(2).ToString(L"D"));
tuesday1 = double::Parse(Console::ReadLine());
}
catch(FormatException ^)
{
Console::WriteLine(L"You typed an invalid value");
}
try {
Console::Write(L"{0}: ",
payroll->StartPeriod.AddDays(3).ToString(L"D"));
wednesday1 = double::Parse(Console::ReadLine());
}
catch(FormatException ^)
{
Console::WriteLine(L"You typed an invalid value");
}
try {
Console::Write(L"{0}: ",
payroll->StartPeriod.AddDays(4).ToString(L"D"));
thursday1 = double::Parse(Console::ReadLine());
}
catch(FormatException ^)
{
Console::WriteLine(L"You typed an invalid value");
}
try {
Console::Write(L"{0}: ",
payroll->StartPeriod.AddDays(5).ToString(L"D"));
friday1 = double::Parse(Console::ReadLine());
}
catch(FormatException ^)
{
Console::WriteLine(L"You typed an invalid value");
}
Console::WriteLine(L"=-= Week 2 =-=");
try {
Console::Write(L"{0}: ",
payroll->StartPeriod.AddDays(8).ToString(L"D"));
monday2 = double::Parse(Console::ReadLine());
}
catch(FormatException ^)
{
Console::WriteLine(L"You typed an invalid value");
}
try {
Console::Write(L"{0}: ",
payroll->StartPeriod.AddDays(9).ToString(L"D"));
tuesday2 = double::Parse(Console::ReadLine());
}
catch(FormatException ^)
{
Console::WriteLine(L"You typed an invalid value");
}
try {
Console::Write(L"{0}: ",
payroll->StartPeriod.AddDays(10).ToString(L"D"));
wednesday2 = double::Parse(Console::ReadLine());
}
catch(FormatException ^)
{
Console::WriteLine(L"You typed an invalid value");
}
try {
Console::Write(L"{0}: ",
payroll->StartPeriod.AddDays(11).ToString(L"D"));
thursday2 = double::Parse(Console::ReadLine());
}
catch(FormatException ^)
{
Console::WriteLine(L"You typed an invalid value");
}
try {
Console::Write(L"{0}: ",
payroll->StartPeriod.AddDays(12).ToString(L"D"));
friday2 = double::Parse(Console::ReadLine());
}
catch(FormatException ^)
{
Console::WriteLine(L"You typed an invalid value");
}
// Calculate the total number of hours for each week
totalHoursWeek1 = monday1 + tuesday1 + wednesday1 +
thursday1 + friday1;
totalHoursWeek2 = monday2 + tuesday2 + wednesday2 +
thursday2 + friday2;
// The overtime is paid time and half
double ovtSalary = payroll->HourlySalary * 1.5;
// If the employee worked under 40 hours,
// there is no overtime
if( totalHoursWeek1 < 40 )
{
regHours1 = totalHoursWeek1;
regAmount1 = payroll->HourlySalary * regHours1;
ovtHours1 = 0.00;
ovtAmount1 = 0.00;
} // If the employee worked over 40 hours,
// calculate the overtime
else if( totalHoursWeek1 >= 40 )
{
regHours1 = 40;
regAmount1 = payroll->HourlySalary * 40;
ovtHours1 = totalHoursWeek1 - 40;
ovtAmount1 = ovtHours1 * ovtSalary;
}
if( totalHoursWeek2 < 40 )
{
regHours2 = totalHoursWeek2;
regAmount2 = payroll->HourlySalary * regHours2;
ovtHours2 = 0.00;
ovtAmount2 = 0.00;
}
else if( totalHoursWeek2 >= 40 )
{
regHours2 = 40;
regAmount2 = payroll->HourlySalary * 40;
ovtHours2 = totalHoursWeek2 - 40;
ovtAmount2 = ovtHours2 * ovtSalary;
}
regularHours = regHours1 + regHours2;
overtimeHours = ovtHours1 + ovtHours2;
regularAmount = regAmount1 + regAmount2;
overtimeAmount = ovtAmount1 + ovtAmount2;
totalEarnings = regularAmount + overtimeAmount;
payroll->Week1Monday = monday1;
payroll->Week1Tuesday = tuesday1;
payroll->Week1Wednesday = wednesday1;
payroll->Week1Thursday = thursday1;
payroll->Week1Friday = friday1;
payroll->Week2Monday = monday2;
payroll->Week2Tuesday = tuesday2;
payroll->Week2Wednesday = wednesday2;
payroll->Week2Thursday = thursday2;
payroll->Week2Friday = friday2;
payroll->RegularHours = regularHours;
payroll->OvertimeHours = overtimeHours;
payroll->RegularAmount = regularAmount;
payroll->OvertimeAmount = overtimeAmount;
payroll->TotalEarnings = totalEarnings;
ShowPayroll(payroll);
Console::Write(L"Do you want to save "
L"the payroll (y/n): ");
String ^ strAnswer = Console::ReadLine();
if( strAnswer->ToUpper() == L"Y")
SavePayroll(payroll);
}
void SavePayroll(CPayrollInformation ^ pay)
{
// We will need this value to create the
// name of the payroll file
String ^ strMonth = L"0", ^strDay = L"0", ^strYear = L"0";
// We want the month and day to include 0 if necessary
strMonth = pay->StartPeriod.Month.ToString();
if( pay->StartPeriod.Month < 10 )
strMonth = L"0" + pay->StartPeriod.Month.ToString();
strDay = pay->StartPeriod.Day.ToString();
if( pay->StartPeriod.Day < 10 )
strDay = L"0" + pay->StartPeriod.Day.ToString();
strYear = pay->StartPeriod.Year.ToString();
String ^ strPayrollFilename = L"C:\\Georgetown "
L"Cleaning Services\\Payrolls\\"
+ pay->LastName[0] +
pay->FirstName[0] +
strMonth + strDay +
strYear + ".epr";
try {
// If there is not yet a directory for the
// payrolls, then create it
Directory::CreateDirectory(L"C:\\Georgetown Cleaning "
L"Services\\Payrolls");
}
catch(DirectoryNotFoundException ^)
{
Console::WriteLine(L"The employee payroll file "
L"could not be created");
}
if( File::Exists(strPayrollFilename) )
{
Console::WriteLine(L"The employee's payroll "
L"for that period exists already");
}
FileStream ^ fsEmployeePayroll =
gcnew FileStream(strPayrollFilename,
FileMode::Create);
BinaryFormatter ^ bfEmployeePayroll =
gcnew BinaryFormatter();
bfEmployeePayroll->Serialize(fsEmployeePayroll, pay);
fsEmployeePayroll->Close();
}
void ShowPayroll(CPayrollInformation ^ payed)
{
Console::WriteLine(L"\n============================="
L"===================");
Console::WriteLine(L"=$= Payroll summary =$=");
Console::WriteLine(L"-------------------------------"
L"-----------------");
Console::WriteLine(L"Employee #: {0}",
payed->EmployeeNumber);
Console::WriteLine(L"Full Name: {0}, {1}",
payed->FirstName, payed->LastName);
Console::WriteLine(L"Hourly Salary: {0:C}",
payed->HourlySalary);
Console::WriteLine(L"Start Period: {0:D}",
payed->StartPeriod);
Console::WriteLine(L"End Period: {0:D}",
payed->EndPeriod);
Console::WriteLine(L"--------------------------------"
L"----------------");
Console::WriteLine(L" Monday Tuesday Wednesday "
L"Thursday Friday");
Console::WriteLine(L"Week 1: {0:F} {1:F} "
L"{2:F} {3:F} {4:F}",
payed->Week1Monday, payed->Week1Tuesday,
payed->Week1Wednesday, payed->Week1Thursday,
payed->Week1Friday);
Console::WriteLine(L"Week 2: {0:F} {1:F} "
L"{2:F} {3:F} {4:F}",
payed->Week2Monday, payed->Week2Tuesday,
payed->Week2Wednesday, payed->Week2Thursday,
payed->Week2Friday);
Console::WriteLine(L"-------------------------------"
L"-----------------");
Console::WriteLine(L"Monetary Summary");
Console::WriteLine(L" Hours Amount");
Console::WriteLine(L"Regular: {0,6} {1,6}",
payed->RegularHours.ToString(L"F"),
payed->RegularAmount.ToString(L"F"));
Console::WriteLine(L"Overtime: {0,6} {1,6}",
payed->OvertimeHours.ToString(L"F"),
payed->OvertimeAmount.ToString(L"F"));
Console::WriteLine(L"-------------------------------"
L"-----------------");
Console::WriteLine(L"Net Pay: {0:F}",
payed->TotalEarnings);
Console::WriteLine(L"==============================="
L"=================\n");
}
void ViewPayroll()
{
}
int main()
{
wchar_t answer = L'0';
Console::WriteLine(L"========================"
L"========================");
Console::WriteLine(L"Georgetown Cleaning Services");
Console::WriteLine(L"========================"
L"========================");
do {
try {
Console::WriteLine(L"\nWhat do you want to do?");
Console::WriteLine(L"0. Quit");
Console::WriteLine(L"1. Hire a new employee");
Console::WriteLine(L"2. Process a payroll");
Console::WriteLine(L"3. View an employee's payroll");
Console::Write(L"Your Choice: ");
answer = wchar_t::Parse(Console::ReadLine());
Console::WriteLine();
}
catch(FormatException ^)
{
Console::WriteLine(L"Invalid Answer!");
}
switch(answer)
{
case L'1':
HireEmployee();
break;
case L'2':
CreatePayroll();
break;
case L'3':
ViewPayroll();
break;
default:
break;
}
} while( (answer == L'1') ||
(answer == L'2') ||
(answer == L'3') );
Console::WriteLine();
return 0;
}
|
-
Execute the application and test it. Here is an example:
================================================
Georgetown Cleaning Services
================================================
What do you want to do?
0. Quit
1. Hire a new employee
2. Process a payroll
3. View an employee's payroll
Your Choice: 2
Enter Employee Number: 29-368
------------------------------------------------
Employee #: 29-368
Full Name: Monay, Gertrude
Hourly Salary: $10.85
------------------------------------------------
Enter Payroll Start Date (mm/dd/yyyy): 11/12/05
Invalid Date Entry
Payrolls start on a Sunday
Enter Payroll Start Date (mm/dd/yyyy): 11/12/06
Enter the time worked for each day (0.00)
=-= Week 1 =-=
Monday, November 13, 2006: 8.00
Tuesday, November 14, 2006: 8.50
Wednesday, November 15, 2006: 9.50
Thursday, November 16, 2006: 8
Friday, November 17, 2006: 8.50
=-= Week 2 =-=
Monday, November 20, 2006: 6.50
Tuesday, November 21, 2006: 7.00
Wednesday, November 22, 2006: 8
Thursday, November 23, 2006: 6.00
Friday, November 24, 2006: 7.00
================================================
=$= Payroll summary =$=
------------------------------------------------
Employee #: 29-368
Full Name: Monay, Gertrude
Hourly Salary: $10.85
Start Period: Sunday, November 12, 2006
End Period: Saturday, November 25, 2006
------------------------------------------------
Monday Tuesday Wednesday Thursday Friday
Week 1: 8.00 8.50 9.50 8.00 8.50
Week 2: 6.50 7.00 8.00 6.00 7.00
------------------------------------------------
Monetary Summary
Hours Amount
Regular: 74.50 808.33
Overtime: 2.50 40.69
------------------------------------------------
Net Pay: 849.01
================================================
Do you want to save the payroll (y/n): Y
What do you want to do?
0. Quit
1. Hire a new employee
2. Process a payroll
3. View an employee's payroll
Your Choice: 0
Press any key to continue . . .
|
-
Close the DOS window
-
Execute the application again and process another payroll. Here is an
example:
================================================
Georgetown Cleaning Services
================================================
What do you want to do?
0. Quit
1. Hire a new employee
2. Process a payroll
3. View an employee's payroll
Your Choice: 2
Enter Employee Number: 86-025
There is no employee with that number in our records
What do you want to do?
0. Quit
1. Hire a new employee
2. Process a payroll
3. View an employee's payroll
Your Choice: 2
Enter Employee Number: 86-225
------------------------------------------------
Employee #: 86-225
Full Name: Harang, Anne
Hourly Salary: $16.75
------------------------------------------------
Enter Payroll Start Date (mm/dd/yyyy): 11/26/2006
Enter the time worked for each day (0.00)
=-= Week 1 =-=
Monday, November 27, 2006: 8
Tuesday, November 28, 2006: 6.5
Wednesday, November 29, 2006: 8.5
Thursday, November 30, 2006: 8
Friday, December 01, 2006: 8
=-= Week 2 =-=
Monday, December 04, 2006: 9
Tuesday, December 05, 2006: 8.5
Wednesday, December 06, 2006: 8
Thursday, December 07, 2006: 9.5
Friday, December 08, 2006: 8.00
================================================
=$= Payroll summary =$=
------------------------------------------------
Employee #: 86-225
Full Name: Anne, Harang
Hourly Salary: $16.75
Start Period: Sunday, November 26, 2006
End Period: Saturday, December 09, 2006
------------------------------------------------
Monday Tuesday Wednesday Thursday Friday
Week 1: 8.00 6.50 8.50 8.00 8.00
Week 2: 9.00 8.50 8.00 9.50 8.00
------------------------------------------------
Monetary Summary
Hours Amount
Regular: 79.00 1323.25
Overtime: 3.00 75.38
------------------------------------------------
Net Pay: 1398.63
================================================
Do you want to save the payroll (y/n):
|
-
Close the DOS window
As serialization is the process of storing an object to a
medium, the opposite, serialization is used to retrieve an object from a stream.
To support this, the BinaryFormatter class is equipped with the Deserialize()
method. Like Serialize(), the Deserialize() method is overloaded
with two versions. One of them uses the following syntax:
public:
Object ^ Deserialize(Stream ^ serializationStream) sealed;
This method takes as argument a Stream-based object,
such as a FileStream variable, that indicates where the file is located
The Deserialize() method. The Deserialize() method returns an Object
object. As a goal, you want the Deserialize() method to produce the type
of object that was saved so you can retrieve the values that the returned object
holds. Because the method returns an Object value, you must cast the returned
value to the type of your class.
Once the Deserialize() method has returned the desired
object, you can access its values. Here is an example:
using namespace System;
using namespace System::IO;
using namespace System::Runtime::Serialization::Formatters::Binary;
[Serializable]
public ref class CCar
{
public:
String ^Make;
String ^Model;
int Year;
int Color;
};
int main()
{
FileStream ^ stmCar = gcnew FileStream(L"LexusLS.car",
FileMode::Open);
BinaryFormatter ^ bfmCar = gcnew BinaryFormatter();
CCar ^ vehicle = dynamic_cast<CCar ^>(bfmCar->Deserialize(stmCar));
Console::WriteLine(L"Make: {0}", vehicle->Make);
Console::WriteLine(L"Model: {0}", vehicle->Model);
Console::WriteLine(L"Year: {0}", vehicle->Year);
Console::Write(L"Color: ");
int clr = vehicle->Color;
switch(clr)
{
case 1:
Console::WriteLine(L"Black");
break;
case 2:
Console::WriteLine(L"Gray");
break;
case 3:
Console::WriteLine(L"White");
break;
case 4:
Console::WriteLine(L"Red");
break;
case 5:
Console::WriteLine(L"Blue");
break;
}
stmCar->Close();
return 0;
}
This would produce:
Make: Lexus
Model: LS
Year: 2007
Color: Red
Press any key to continue . . .
|
 Practical
Learning: De-Serializing an Object Practical
Learning: De-Serializing an Object
|
|
- In the Exercise.cpp file, implement the ViewPayroll() function as follows:
void ViewPayroll()
{
String ^ strEmplNumber, ^strFName, ^strLName;
String ^ strMonth, ^strDay, ^strYear;
// Ask the clerk to enter an employee number
// using the format 00-000
Console::Write(L"Enter Employee Number (00-000): ");
strEmplNumber = Console::ReadLine();
String ^ strFilename = L"C:\\Georgetown Cleaning "
L"Services\\Employees\\"
+ strEmplNumber + ".gce";
if( !File::Exists(strFilename) )
{
Console::Write(L"There is no employee "
L"with that number.");
}
else
{
FileStream ^ fsEmployee = nullptr;
BinaryReader ^ brEmployee = nullptr;
try {
// We need to formally open the file
// because we need the employees initials
fsEmployee = gcnew FileStream(strFilename,
FileMode::Open,
FileAccess::Read);
brEmployee = gcnew BinaryReader(fsEmployee);
// Read the file, mainly to get the
// employee's name
strEmplNumber = brEmployee->ReadString();
strFName = brEmployee->ReadString();
strLName = brEmployee->ReadString();
}
finally
{
brEmployee->Close();
fsEmployee->Close();
}
Console::Write(L"Enter the start date of the "
L"payroll you want to see (mm/dd/yyyy): ");
DateTime dteStartDate =
DateTime::Parse(Console::ReadLine());
// We want the month and day to include 0 if necessary
strMonth = dteStartDate.Month.ToString();
if( dteStartDate.Month < 10 )
strMonth = L"0" + dteStartDate.Month.ToString();
strDay = dteStartDate.Day.ToString();
if( dteStartDate.Day < 10 )
strDay = L"0" + dteStartDate.Day.ToString();
strYear = dteStartDate.Year.ToString();
strFilename = L"C:\\Georgetown Cleaning "
L"Services\\Payrolls\\"
+ strLName[0] +
strFName[0] + strMonth +
strDay + strYear + ".epr";
if( !File::Exists(strFilename) )
{
Console::Write(L"{0}, {1} doesn't have a "
L"payroll in that time frame",
strLName, strFName);
}
else
{
// Open the payroll and display it
FileStream ^ fsPayroll =
gcnew FileStream(strFilename,
FileMode::Open);
BinaryFormatter ^ bfPayroll =
gcnew BinaryFormatter();
CPayrollInformation ^ pay =
dynamic_cast<CPayrollInformation ^>
(bfPayroll->Deserialize(fsPayroll));
ShowPayroll(pay);
}
}
}
|
-
Execute the application and test it. Here is an example:
================================================
Georgetown Cleaning Services
================================================
What do you want to do?
0. Quit
1. Hire a new employee
2. Process a payroll
3. View an employee's payroll
Your Choice: 3
Enter Employee Number (00-000): 29-368
Enter the start date of the payroll you want to see (mm/dd/yyyy): 11/12/06
================================================
=$= Payroll summary =$=
------------------------------------------------
Employee #: 29-368
Full Name: Gertrude, Monay
Hourly Salary: $10.85
Start Period: Sunday, November 12, 2006
End Period: Saturday, November 25, 2006
------------------------------------------------
Monday Tuesday Wednesday Thursday Friday
Week 1: 8.00 8.50 9.50 8.00 8.50
Week 2: 6.50 7.00 8.00 6.00 7.00
------------------------------------------------
Monetary Summary
Hours Amount
Regular: 74.50 808.33
Overtime: 2.50 40.69
------------------------------------------------
Net Pay: 849.01
================================================
What do you want to do?
0. Quit
1. Hire a new employee
2. Process a payroll
3. View an employee's payroll
Your Choice: 0
Press any key to continue . . .
|
-
Close the DOS window
|
|

