Introduction to XML Elements
 |
Introduction to XML Elements |
|
Elements Fundamentals |
|
Introduction |
|
An element in an XML document is an object that begins with a start-tag, may contain a value, and may terminate with an }-tag. Based on this, the combination of a start-tag, the value, and the end-tag is called an element. An element can be more than that but for now, we will consider that an element is primarily characterized by a name and possibly a value. To support XML elements, the System.Xml namespace provides the XmlElement class. XmlElement is based on a class named XmlLinkedNode that itself is based on XmlNode. To access an XML element, you can declare a variable of type XmlElement but the main purpose of this class is to get an element from a DOM object. For this reason, the XmlElement class doesn't have a constructor you can use. Instead, and as we will learn, the other classes have methods that produce an XmlElement element you can manipulate as necessary. |
|
In the previous lesson, we saw that every XML file must have a root and we mentioned that you could call the XmlDocument::DocumentElement property to access it. This property is of type XmlElement and, to access it, you can declare an XmlElement variable and assign it this property. Here is an example:
#pragma once
#include <windows.h>
#using <System.dll>
#using <System.Xml.dll>
#using <System.Drawing.dll>
#using <System.Windows.Forms.dll>
using namespace System;
using namespace System::Xml;
using namespace System::Drawing;
using namespace System::Windows::Forms;
using namespace System::IO;
public ref class CExercise : public Form
{
private:
Button ^ btnDocument;
void btnDocumentClicked(Object ^ sender, EventArgs ^ e);
void InitializeComponents();
public:
CExercise();
};
CExercise::CExercise()
{
InitializeComponents();
}
void CExercise::InitializeComponents()
{
btnDocument = gcnew Button();
btnDocument->Location = Point(20, 20);
btnDocument->Text = L"Document";
btnDocument->Click += gcnew EventHandler(this, &CExercise::btnDocumentClicked);
Controls->Add(btnDocument);
}
void CExercise::btnDocumentClicked(Object ^ sender, EventArgs ^ e)
{
String ^ strFilename = L"videos.xml";
XmlDocument ^ docVideo = gcnew XmlDocument;
if (File::Exists(strFilename))
{
docVideo->Load(strFilename);
XmlElement ^ elm = docVideo->DocumentElement;
}
else
MessageBox::Show(L"The file " + strFilename + L" was not found");
}
int APIENTRY WinMain(HINSTANCE hInstance, HINSTANCE hPrevInstance,
LPSTR lpCmdLine, int nCmdShow)
{
Application::Run(gcnew CExercise());
return 0;
}
An XML element is represented in the XmlNodeType enumeration as the Element member. When using the Read() method of an XmlTextReader object, to find out if the item being read is an element, you can check whether the member of the current XmlNodeType is Element. Here is an example: void CExercise::btnDocumentClicked(Object ^ sender, EventArgs ^ e)
{
String ^ strFilename = L"videos.xml";
XmlDocument ^ docVideo = gcnew XmlDocument;
if (File::Exists(strFilename))
{
XmlTextReader ^ rdrVideos = gcnew XmlTextReader(strFilename);
do
{
switch (rdrVideos->NodeType)
{
case XmlNodeType::Element:
break;
}
} while (rdrVideos->Read());
}
else
MessageBox::Show(L"The file " + strFilename + L" was not found");
}
The name of an element is the string that represents the tag. For example, in <Director>, the word Director is the name of the element. An element must have at least a start-tag. All of the tags we have seen so far were created as elements. When creating your elements, remember to follow the rules we defined for names. The XmlElement class is equipped with the Name property that can be used to identify an existing element. Here is an example of accessing it: void CExercise::btnDocumentClicked(Object ^ sender, EventArgs ^ e)
{
String ^ strFilename = L"videos.xml";
XmlDocument ^ docVideo = gcnew XmlDocument;
if (File::Exists(strFilename))
{
docVideo->Load(strFilename);
XmlElement ^ elm = docVideo->DocumentElement;
MessageBox::Show(elm->Name);
}
else
MessageBox::Show(L"The file " + strFilename + L" was not found");
}
This would produce:
Notice that videos is returned as the name of the root element of the document. If calling the Read() method of an XmlTextReader object to scan a file, when you get to an element, you can find out its Name identity by accessing it. Here is an example: void CExercise::btnDocumentClicked(Object ^ sender, EventArgs ^ e)
{
String ^ strFilename = L"videos.xml";
XmlDocument ^ docVideo = gcnew XmlDocument;
if (File::Exists(strFilename))
{
XmlTextReader ^ rdrVideos = gcnew XmlTextReader(strFilename);
do
{
switch (rdrVideos->NodeType)
{
case XmlNodeType::Element:
MessageBox::Show(rdrVideos->Name);
break;
}
} while (rdrVideos->Read());
}
else
MessageBox::Show(L"The file " + strFilename + L" was not found");
}
The value of an element is the item displayed on the right side of the start-tag. It is also called the text of the element. In the case of <director>Jonathan Lynn</director>, the "Jonathan Lynn" string is the value of the director element. To support the text or value of an element, the XmlElement class is equipped with the Value property. While the value of one element can be a number, the value of another element can be a date. Yet another element can use a regular string as its value. Consider the following example: <?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<videos>
<video>
<title>The Distinguished Gentleman</title>
<director>Jonathan Lynn</director>
<LengthInMinutes>112</LengthInMinutes>
<format>DVD</format>
<rating>R</rating>
<price>14.95</price>
</video>
<video>
<title>Her Alibi</title>
<director>Bruce Beresford</director>
<LengthInMinutes>94</LengthInMinutes>
<format>VHS</format>
<rating>PG-13</rating>
<price>9.95</price>
</video>
</videos>
Notice that the price elements contain numbers that look like currency values and the LengthInMinutes elements use an integer as value. If you are using an XmlTextReader object to scan a file, when the Read() method gets to an element, you can find out what its value is by accessing this property. Here is an example: void CExercise::btnDocumentClicked(Object ^ sender, EventArgs ^ e)
{
String ^ strFilename = L"videos.xml";
XmlDocument ^ docVideo = gcnew XmlDocument;
if (File::Exists(strFilename))
{
XmlTextReader ^ rdrVideos = gcnew XmlTextReader(strFilename);
do
{
switch (rdrVideos->NodeType)
{
case XmlNodeType::Text:
MessageBox::Show(rdrVideos->Value);
break;
}
} while (rdrVideos->Read());
}
else
MessageBox::Show(L"The file " + strFilename + L" was not found");
}
The value or text of an element is an object of type XmlText.
An element may not have a value but only a name. Consider the following example: <?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<videos>
<video>
<title>The Distinguished Gentleman</title>
<director>Jonathan Lynn</director>
</video>
</videos>
In this case, the video element does not have a value. It is called an empty element. When a tag is empty, the Value property of its XmlElement object would return an empty value.
Besides the obvious types of values, you may want to display special characters as values of elements. Consider the following example: <?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8" ?>
<Employees>
<Employee>
<FullName>Sylvie <Bellie> Aronson</FullName>
<Salary>25.64</Salary>
<DepartmentID>1</DepartmentID>
</Employee>
<Employee>
<FullName>Bertrand Yamaguchi</FullName>
<Salary>16.38</Salary>
<DepartmentID>4</DepartmentID>
</Employee>
</Employees>
If you try using this XML document, for example, if you try displaying it in a browser, you would receive an error:
The reason is that when the parser reaches the <FullName>Sylvie <Bellie> Aronson</FullName> line, it thinks that <Bellie> is a tag but then <Bellie> is not closed. The parser concludes that the document is not well-formed, that there is an error. For this reason, to display a special symbol as part of a value, you can use its character code. For example, the < (less than) character is represented with < and the > (greater than) symbol can be used with >. Therefore, the above code can be corrected as follows: <?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8" ?>
<Employees>
<Employee>
<FullName>Sylvie <Bellie> Aronson</FullName>
<Salary>25.64</Salary>
<DepartmentID>1</DepartmentID>
</Employee>
<Employee>
<FullName>Bertrand Yamaguchi</FullName>
<Salary>16.38</Salary>
<DepartmentID>4</DepartmentID>
</Employee>
</Employees>
This would produce:
Here is a list of other codes you can use for special characters:
There are still other codes to include special characters in an XML file.
In the previous sections, we have seen how to create a tag to produce a node. We also saw that a node could be placed inside of another node. The combined text of the values of the children of a node is available through its XmlNode::InnerText property which is declared as follows: public:
virtual property String^ InnerText
{
String^ get ();
void set (String ^ value);
}
This property concatenates the values of the children of the node that called them but doesn't include their markups. Here is an example: Void btnDocument_Click(System::Object^ sender, System::EventArgs^ e)
{
XmlDocument ^ docVideo = gcnew XmlDocument;
String ^ strFilename = L"videos.xml";
if (File::Exists(strFilename))
{
docVideo->Load(strFilename);
XmlElement ^ elm = docVideo->DocumentElement;
txtDocument->Text = elm->InnerText;
}
else
MessageBox::Show(L"The file " + strFilename + L" was not found");
}
This would produce:
Notice that this property produces all values of the children of a node in one block. We already saw how to access each value of the children of a node by calling the XmlTextReader::Read() method and get its Text.
If you want to get a node, its markup, its child(ren) and its(their) markup(s), you can access its XmlNode::OuterXml property which is declared as follows: public:
virtual property String^ OuterXml
{
String^ get ();
}
Here is an example: Void btnDocument_Click(System::Object^ sender, System::EventArgs^ e)
{
XmlDocument ^ docVideo = gcnew XmlDocument;
String ^ strFilename = L"videos.xml";
if (File::Exists(strFilename))
{
docVideo->Load(strFilename);
XmlElement ^ elm = docVideo->DocumentElement;
txtDocument->Text = elm->OuterXml;
}
else
MessageBox::Show(L"The file " + strFilename + L" was not found");
}
This would produce:
If you want only the markup(s) of the child(ren) excluding the parent, access its XmlNode::InnerXml property which is declared as follows: public:
virtual property String^ InnerXml
{
String^ get();
void set(String^ value);
}
Here is an example: Void btnDocument_Click(System::Object^ sender, System::EventArgs^ e)
{
XmlDocument ^ docVideo = gcnew XmlDocument;
String ^ strFilename = L"videos.xml";
if (File::Exists(strFilename))
{
docVideo->Load(strFilename);
XmlElement ^ elm = docVideo->DocumentElement;
txtDocument->Text = elm->InnerXml;
}
else
MessageBox::Show(L"The file " + strFilename + L" was not found");
}
This would produce:
As mentioned already, one node can be nested inside of another. A nested node is called a child of the nesting node. This also implies that a node can have as many children as necessary, making them child nodes of the parent node. Once again, consider our videos.xml example: <?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<videos>
<video>
<title>The Distinguished Gentleman</title>
<director>Jonathan Lynn</director>
<length>112 Minutes</length>
<format>DVD</format>
<rating>R</rating>
</video>
<video>
<title>Her Alibi</title>
<director>Bruce Beresford</director>
<length>94 Mins</length>
<format>DVD</format>
<rating>PG-13</rating>
</video>
<video>
<title>Chalte Chalte</title>
<director>Aziz Mirza</director>
<length>145 Mins</length>
<format>DVD</format>
<rating>N/R</rating>
</video>
</videos>
The title and the director nodes are children of the video node. The video node is the parent of both the title and the director nodes.
To support the child nodes of a particular node, the XmlNode class is equipped with a property named ChildNodes. To identify the collection of child nodes of a node, the .NET Framework provides the XmlNodeList class. Therefore, the ChildNodes property of an XmlNode object is of type XmlNodeList. This property is declared as follows: public:
virtual property XmlNodeList^ ChildNodes
{
XmlNodeList^ get ();
}
When this property is used, it produces an XmlNodeList list, which is a collection of all nodes that share the same parent. Each item in the collection is of type XmlNode. To give you the number of nodes on an XmlNodeList collection, the class is equipped with a property named Count. Here is an example of using it: Void btnDocument_Click(System::Object^ sender, System::EventArgs^ e)
{
XmlDocument ^ docVideo = gcnew XmlDocument;
String ^ strFilename = L"videos.xml";
if (File::Exists(strFilename))
{
docVideo->Load(strFilename);
XmlElement ^ elm = docVideo->DocumentElement;
XmlNodeList ^ lstVideos = elm->ChildNodes;
MessageBox::Show("The root element contains " +
lstVideos->Count + L" nodes");
}
else
MessageBox::Show(L"The file " + strFilename + L" was not found");
}
This would produce:
You can also use the Count property in a for loop to visit the members of the collection. The children of a node, that is, the members of a ChildNodes property, or the members of an XmlNodeList collection, can be located each by an index. The first node has an index of 0, the second has an index of 1, an so on. To give you access to a node of the collection, the XmlNodeList class is equipped with an indexed property and a method named Item. Both produce the same result. For example, if a node has three children, to access the third, you can apply an index of 2 to its indexed property. Here is an example: Void btnDocument_Click(System::Object^ sender, System::EventArgs^ e)
{
XmlDocument ^ docVideo = gcnew XmlDocument;
String ^ strFilename = L"videos.xml";
if (File::Exists(strFilename))
{
docVideo->Load(strFilename);
XmlElement ^ elm = docVideo->DocumentElement;
XmlNodeList ^ lstVideos = elm->ChildNodes;
MessageBox::Show(lstVideos[2]->InnerText);
}
else
MessageBox::Show(L"The file " + strFilename + L" was not found");
}
You can also use the Item() method to get the same result. Using a for loop, you can access each node and display the values of its children as follows: Void btnDocument_Click(System::Object^ sender, System::EventArgs^ e)
{
XmlDocument ^ docVideo = gcnew XmlDocument;
String ^ strFilename = L"videos.xml";
if (File::Exists(strFilename))
{
docVideo->Load(strFilename);
XmlElement ^ elm = docVideo->DocumentElement;
XmlNodeList ^ lstVideos = elm->ChildNodes;
for(int i = 0; i < lstVideos->Count; i++)
MessageBox::Show(lstVideos[i]->InnerText);
}
else
MessageBox::Show(L"The file " + strFilename + L" was not found");
}
Instead of using the indexed property, the XmlNodeList class implements the IEnumerable interface. This allows you to use a for each loop to visit each node of the collection. Here is an example: Void btnDocument_Click(System::Object^ sender, System::EventArgs^ e)
{
XmlDocument ^ docVideo = gcnew XmlDocument;
String ^ strFilename = L"videos.xml";
if (File::Exists(strFilename))
{
docVideo->Load(strFilename);
XmlElement ^ elm = docVideo->DocumentElement;
XmlNodeList ^ lstVideos = elm->ChildNodes;
for each (XmlNode ^ node in lstVideos)
MessageBox::Show(node->InnerText);
}
else
MessageBox::Show(L"The file " + strFilename + L" was not found");
}
To better manage and manipulate the nodes of a collection of nodes, you must be able to access the desired node. The XmlNode class combined with the XmlNodeList class provide various means of getting to a node and taking the appropriate actions.
Not all nodes have children, obviously. For example, the title node of our videos.xml file does not have children. To find out whether a node has children, check its HasChildNodes Boolean property that is declared as follows: public:
virtual property bool HasChildNodes
{
bool get();
}
If a node is a child, to get its parent, you can access its ParentNode property.
The children of a nesting node are also recognized by their sequence. For our videos.xml file, the first line is called the first child of the DOM. This would be: <?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?> After identifying or locating a node, the first node that immediately follows it is referred to as its first child. In our videos.xml file, the first child of the first video node is the <title>The Distinguished Gentleman</title> element. The first child of the second <video> node is <title>Her Alibi</title>. In the .NET Framework, the first child of a node can be retrieved by accessing the XmlNode::FirstChild property declared as follows: public:
virtual property XmlNode^ FirstChild
{
XmlNode^ get();
}
In the following example, every time the parser gets to a video node, it displays the value of it first child: Void btnDocument_Click(System::Object^ sender, System::EventArgs^ e)
{
XmlDocument ^ docVideo = gcnew XmlDocument;
String ^ strFilename = L"videos.xml";
if (File::Exists(strFilename))
{
docVideo->Load(strFilename);
XmlElement ^ elm = docVideo->DocumentElement;
XmlNodeList ^ lstVideos = elm->ChildNodes;
for each (XmlNode ^ node in lstVideos)
lbxVideos->Items->Add(node->FirstChild->InnerText);
}
else
MessageBox::Show(L"The file " + strFilename + L" was not found");
}
This would produce:
In this example, we started our parsing on the root node of the document. At times, you will need to consider only a particular node, such as the first child of a node. For example, you may want to use only the first child of the root. To get it, you can access the FirstChild property of the DocumentElement object of the DOM. Once you get that node, you can then do what you judge necessary. In the following example, only the values of the child nodes of the first child of the root are displayed: Void btnDocument_Click(System::Object^ sender, System::EventArgs^ e)
{
XmlDocument ^ docVideo = gcnew XmlDocument;
String ^ strFilename = L"videos.xml";
if (File::Exists(strFilename))
{
docVideo->Load(strFilename);
XmlNode ^ node = docVideo->DocumentElement->FirstChild;
XmlNodeList ^ lstVideos = node->ChildNodes;
for each (XmlNode ^ child in node->ChildNodes)
lbxVideos->Items->Add(child->InnerText);
}
else
MessageBox::Show(L"The file " + strFilename + L" was not found");
}
This would produce:
Consider the following modification of the Videos.xml file: <?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8" ?>
<Videos>
<Video>
<Title>The Distinguished Gentleman</Title>
<Director>Jonathan Lynn</Director>
<CastMembers>
<Actor>Eddie Murphy</Actor>
<Actor>Lane Smith</Actor>
<Actor>Sheryl Lee Ralph</Actor>
<Actor>Joe Don Baker</Actor>
<Actor>Victoria Rowell</Actor>
</CastMembers>
<Length>112 Minutes</Length>
<Format>DVD</Format>
<Rating>R</Rating>
</Video>
<Video>
<Title>Her Alibi</Title>
<Director>Bruce Beresford</Director>
<Length>94 Minutes</Length>
<Format>DVD</Format>
<Rating>PG-13</Rating>
</Video>
<Video>
<Title>Chalte Chalte</Title>
<Director>Aziz Mirza</Director>
<Length>145 Minutes</Length>
<Format>DVD</Format>
<Rating>N/R</Rating>
</Video>
</Videos>
Remember that when using a for or a for each loop applied to an XmlNodeList collection, each node that you access is a complete XmlNode object and may have children. This means that you can further get the ChildNodes node of any node. Here is an example that primarily scans the nodes but looks for one whose name is CastMembers: private void btnDocument_Click(object sender, EventArgs e)
{
String ^ strFilename = L"videos.xml";
XmlDocument ^ docVideo = gcnew XmlDocument;
if (File::Exists(strFilename))
{
docVideo->Load(strFilename);
// Locate the root node and
// get a reference to its first child
XmlNode ^ node = docVideo->DocumentElement->FirstChild;
// Create a list of the child nodes of
// the first node under the root
XmlNodeList ^ lstVideos = node->ChildNodes;
// Visit each node
for (int i = 0; i < lstVideos.Count; i++)
{
// Look for a node named CastMembers
if (lstVideos[i]->Name == L"CastMembers")
{
// Once/if you find it,
// 1. Access its first child
// 2. Create a list of its child nodes
XmlNodeList ^ lstActors =
lstVideos[i]->ChildNodes;
// Display the values of the nodes
for (int j = 0; j < lstActors.Count; j++)
lbxVideos->Items->Add(lstActors[j]->InnerText);
}
}
}
else
MessageBox::Show(L"The file " + strFilename + L" was not found");
}
This would produce:
As we have learned that a node or a group of nodes can be nested inside of another node. When you get to a node, you may know or find out that it has children. You may then want to consider only the first child. Here is an example: Void btnDocument_Click(System::Object^ sender, System::EventArgs^ e)
{
String ^ strFilename = L"videos.xml";
XmlDocument ^ docVideo = gcnew XmlDocument;
if (File::Exists(strFilename))
{
docVideo->Load(strFilename);
// Locate the root node and
// get a reference to its first child
XmlNode ^ node = docVideo->DocumentElement->FirstChild;
// Create a list of the child nodes of
// the first node under the root
XmlNodeList ^ lstVideos = node->ChildNodes;
// Visit each node
for (int i = 0; i < lstVideos->Count; i++)
{
// Look for a node named CastMembers
if (lstVideos[i]->Name == "CastMembers")
{
// Once/if you find it,
// 1. Access its first child
// 2. Create a list of its child nodes
XmlNodeList ^ lstActors =
lstVideos[i]->FirstChild->ChildNodes;
// Display the value of its first child node
for (int j = 0; j < lstActors->Count; j++)
lbxVideos->Items->Add(lstActors[j]->InnerText);
}
}
}
else
MessageBox::Show(L"The file " + strFilename + L" was not found");
}
This would produce:
As opposed to the first child, the child node that immediately precedes the end-tag of the parent node is called the last child. To get the last child of a node, you can access its XmlNode::LastChild property that is declared as follows: public:
virtual property XmlNode^ LastChild
{
XmlNode^ get ();
}
The child nodes that are nested in a parent node and share the same level are referred to as siblings. Consider the above file: Director, CastMembers, and Length are child nodes of the Video node but the Actor node is not a child of the Video node. Consequently, Director, CastMembers, and Length are siblings. Obviously, to get a sibling, you must first have a node. To access the sibling of a node, you can use its XmlNode::NextSibling property, which is declared as follows: public:
virtual property XmlNode^ NextSibling
{
XmlNode^ get ();
}
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
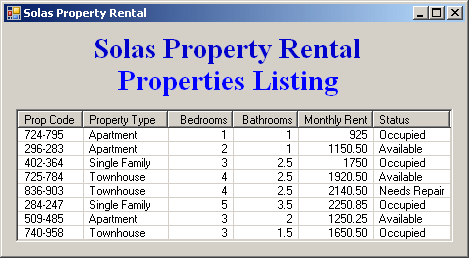
System::Void Form1_Load(System::Object^ sender, System::EventArgs^ e)
{
String ^ strFilename = L"Properties.xml";
XmlDocument ^ docProperties = gcnew XmlDocument;
if (File::Exists(strFilename))
{
docProperties->Load(strFilename);
XmlElement ^ elmProperty = docProperties->DocumentElement;
XmlNodeList ^ lstProperties = elmProperty->ChildNodes;
for each(XmlNode ^ node in lstProperties)
{
ListViewItem ^ lviProperty = gcnew ListViewItem(node->FirstChild->InnerText); // Property code
lviProperty->SubItems->Add(node->FirstChild->NextSibling->InnerText); // Property Type
lviProperty->SubItems->Add(node->FirstChild->NextSibling->NextSibling->InnerText); // Bedrooms
lviProperty->SubItems->Add(node->FirstChild->NextSibling->NextSibling->NextSibling->InnerText); // Bathrooms
lviProperty->SubItems->Add(node->FirstChild->NextSibling->NextSibling->NextSibling->NextSibling->InnerText); // Monthly Rent
lviProperty->SubItems->Add(node->FirstChild->NextSibling->NextSibling->NextSibling->NextSibling->NextSibling->InnerText); // Status
lvwProperties->Items->Add(lviProperty);
}
}
else
MessageBox::Show("The " + strFilename + " file was not found");
}
|
|
|
||
| Previous | Copyright © 2008-2016, FunctionX, Inc. | Next |
|
|
||